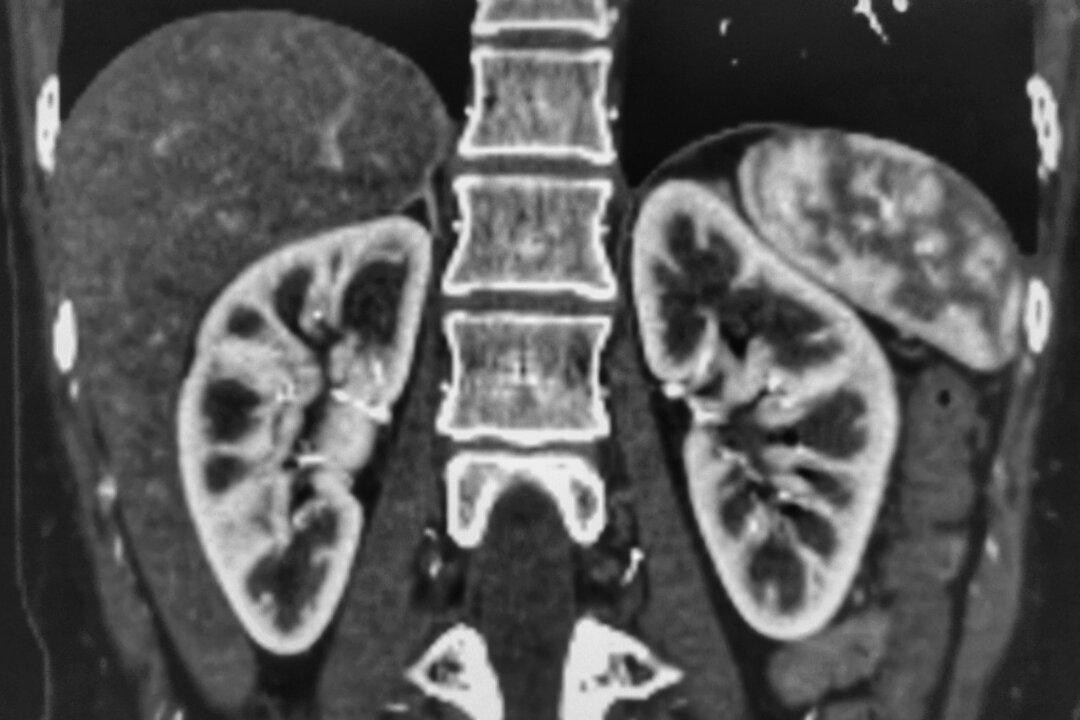
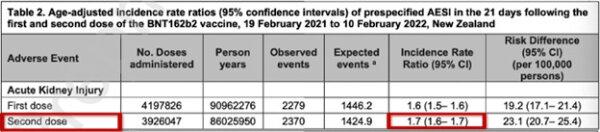
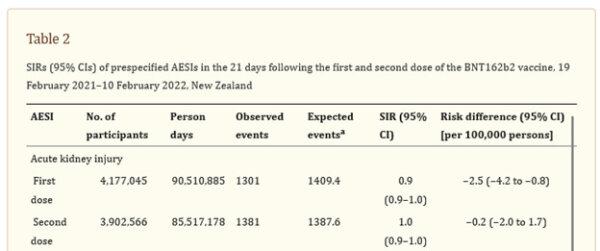
In a January 2023 preprint in The Lancet, the New Zealand government released a study showing a 70 percent increased rate of kidney injury following two doses of Pfizer mRNA vaccines. Even more telling of injury was the dose-dependent effect. That is, one dose of Pfizer showed a 60 percent increased rate of injury within three weeks post-injection, while two doses showed a 70 percent increased rate of injury three weeks post-injection. “Acute kidney injury” was not defined by the authors but is understood in a clinical setting to include measurable changes in lab results and/or serious signs and symptoms such as bleeding, pain with urination, kidney stones, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, or other renal dysfunction.
The data were drawn from a national database of over 4 million people over the age of 5 who had received the Pfizer vaccines. This number represented 95 percent of New Zealand adults and teenagers.
These alarming results of vastly increased kidney injury were published in the abstract of the original article, and here are two screenshots from the January 2023 version of the abstract of that article: [1]
Hiding the Data in New Zealand
Then a strange thing happened to the New Zealand data. Not only did the above paper disappear, but the numbers of reported acute kidney injuries were cut nearly in half. Here is what the same table now shows, from the same-titled paper, by the same authors, since August 2023, [3] at this link:Suddenly, from January to August 2023, the observed acute kidney injury (AKI) events now are only 57 percent and 58 percent, respectively, of the originally reported AKI events. As a result, the data shown in August look like the Pfizer vaccine made no difference or even implied a slight benefit, whereas the data published seven months earlier had shown an alarming increase in acute kidney injuries postvaccine.
Also, in the August 2023 revision, the reported number of those who had received the first dose was reduced by about 100,000, and the number of those receiving the second dose was reduced by over 200,000.
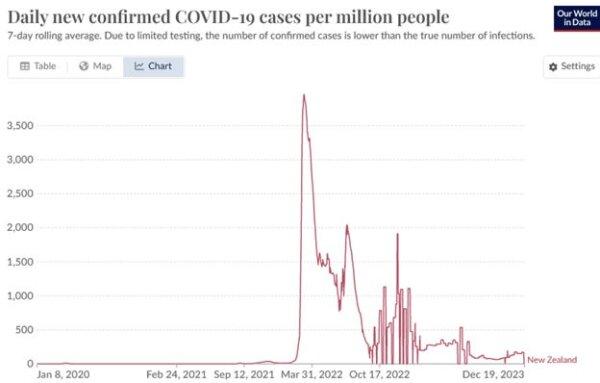
During the time period of the study, Feb. 19, 2021, to Feb. 10, 2022, New Zealand had relatively low rates of COVID-19, as seen in the chart below. [4] The curve below took a vertical turn on Feb. 11, 2022, which was the day after the New Zealand government authors of the paper stopped collecting data. Until that dramatic turn, daily new confirmed COVID cases in New Zealand remained near zero.
- 2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria.
- Acute kidney injury.
- Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody positive.
- Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.
- Autoimmune nephritis.
- Bilirubin urine present.
- C1q nephropathy.
- Chronic autoimmune glomerulonephritis.
- Cryoglobulinaemia.
- Dialysis amyloidosis.
- Fibrillary glomerulonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis membranoproliferative.
- Glomerulonephritis membranous.
- Glomerulonephritis rapidly progressive.
- Goodpasture syndrome.
- Henoch Schonlein purpura nephritis.
- IgA nephropathy.
- IgM nephropathy.
- Immune-mediated nephritis.
- Immune-mediated renal disorder.
- Lupus nephritis.
- Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis.
- Nephritis.
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
- Renal amyloidosis.
- Renal arteritis.
- Renal artery thrombosis.
- Renal embolism.
- Renal failure.
- Renal vascular thrombosis.
- Renal vasculitis.
- Renal vein embolism.
- Renal vein thrombosis.
- Scleroderma renal crisis.
- Tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis syndrome.
- Urine bilirubin increased.
- Urobilinogen urine decreased.
- Urobilinogen urine increased.
- ANCA vasculitis.
- Diffuse vasculitis.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
- Polyarteritis nodosa.
- Pulmonary renal syndrome.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Systemic scleroderma.
- Thrombotic microangiopathy.
- Type III immune complex-mediated hypersensitivity syndrome.

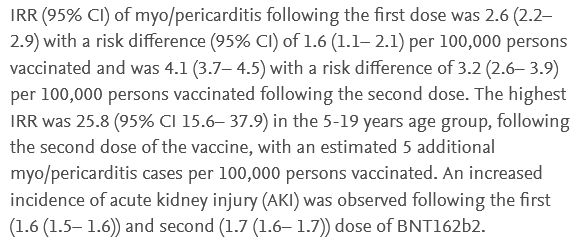
The authors found that 22.5 percent of vaccinated patients experienced new-onset or relapse of glomerulonephritis or other renal events following COVID vaccination. Additionally, 10.8 percent had increased proteinuria, 12.6 percent had worsening hematuria, and 0.9 percent had creatinine values 150 times what is normal or worse.
No difference was found between the Pfizer-vaccinated and Moderna-vaccinated with respect to renal events.
The study found the following:
That study did not discuss the time elapsed from vaccination to glomerulonephritis pathology. This smaller study of 13 patients found that the median time of onset was one week after the first dose and four weeks after the second dose. [7] The patients typically presented with acute kidney injury, edema, and visible blood in the urine.
Several reports of minimal change disease appear in the peer-reviewed literature. [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] Most of those cases occurred within several days of receiving a mRNA COVID vaccine, usually after the second dose, sometimes after the third dose. [15] It has also been seen following the AstraZeneca COVID vaccine. [16]
Minimal change disease is not one of the conditions noted in the Pfizer adverse events list. It is an insidious kidney disorder that is so named for the very subtle changes in the glomeruli filtration, which leaves gaps in filtration. Nephrotic syndrome results, in which proteins leak through the gaps from the blood into the urine, and then systemic effects of hypoproteinemia result.
- Visible blood in the urine (hematuria) within hours after vaccination. [17]
- Membranous nephropathy. [18]
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. [19]
- ANCA glomerulonephritis. [20]
- ANCA vasculitis. [21]
- IgA nephropathy in children. [22]
If You Think the Kidneys Were Hit Hard . . .
After an extensive review of the medical literature over the last three years, since the onset of mass COVID vaccination campaigns, I can say with confidence that the medical literature reveals many fewer victims of kidney injuries following these vaccines than of other types of bodily injuries. Other bodily organs have fared far worse than the kidneys for most of the victims. Most notable and now well-known are the myocarditis and other cardiovascular injuries, for which I described the mechanisms of injury and the ubiquity among the COVID-vaccinated population, [23] as well as brain injuries, [24] among others.Future vaccines must be screened thoroughly for risk to kidneys and other organs before use in adults, and then only with fully detailed and uncoerced informed consent. Clearly, such toxic products as mRNA injections must never be used in children at all and must never be made a condition of work or study for anyone.



No comments:
Post a Comment